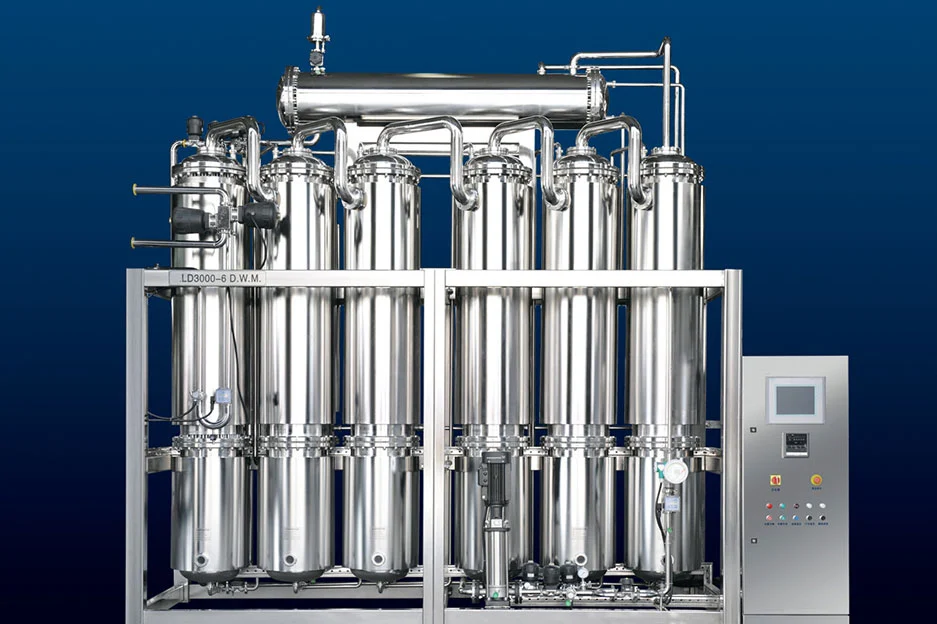
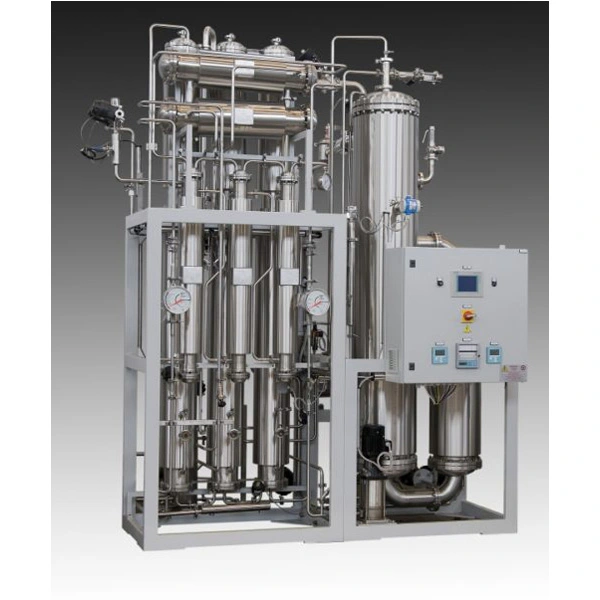
Pharmaceutical purified water systems adopt the latest processes such as reverse osmosis and EDI. Purified water distribution system designs a complete set of purified water process in a targeted manner. The quality of purified water for pharmaceutical manufacturing meets the requirements of the current USP, EP, JP and ChP for purified water.
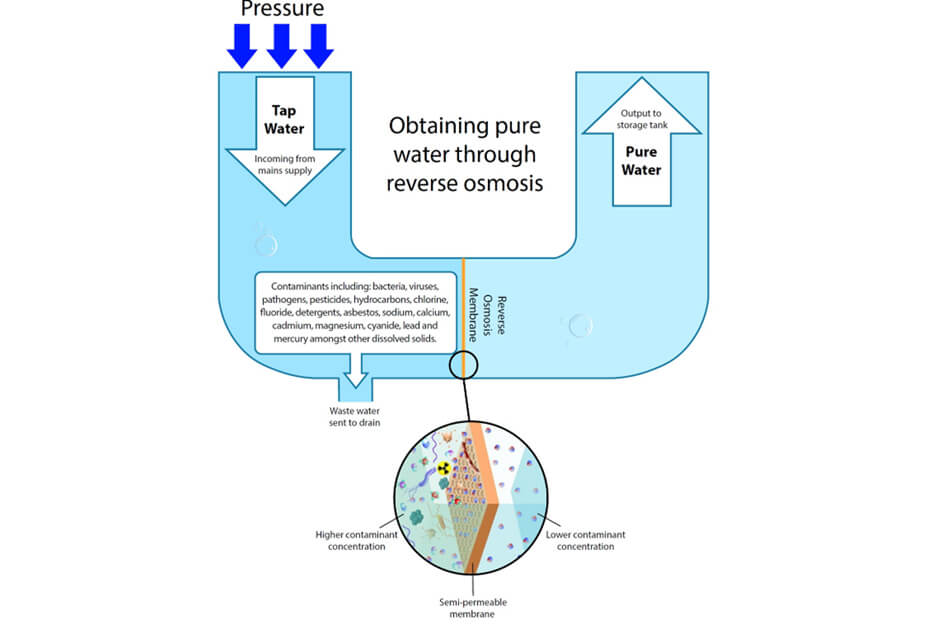
Pretreatment is mainly used to remove particles that may damage the film and free chlorine. The reverse osmosis process is to separate and remove the soluble solids, organics, colloidal substances and bacteria in the water by using the semipermeable spiral membrane. The raw water is sent to and passes through the reverse osmosis membrane under a certain pressure. The water passes through the tiny pore diameter on the membrane and is collected to obtain pure water. Different impurities are concentrated in the intercepting liquid and discharged. RO can remove more than 96% of dissolved solids, more than 99% of organic matters and colloids, and almost 100% of bacteria from raw water.
EDI electromigration removal salt is to use the high voltage of electrodes at both ends of the module to move charged ions in water, and cooperate with ion exchange resin and selective resin membrane to accelerate the removal of ions, so as to achieve the purpose of water purification. During EDI desalination, ions are removed by ion exchange membrane under the action of electric field. At the same time, water molecules generate hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions under the action of electric field, which continuously regenerate the ion exchange resin to keep the ion exchange resin in the best state.
Degassing membranes are widely used to remove oxygen and carbon dioxide from water.
Due to the difference of user's raw water quality, the required purified water process plans will also be quite different (the system can achieve online pasteurization of pretreatment devices; reverse osmosis membranes and EDI modules can choose normal temperature and resistant pasteurization membranes according to requirements; pre-treatment devices can choose to add scale inhibitors or softeners according to requirements; users have high requirements for TOC indicators, and can choose UF (ultrafiltration) to remove TOC at the water production terminal). Based on years of design and practical experience, Biocell has not only been able to design purified water equipment more in line with users' needs, but also developed a purified water energy conservation and emission reduction process scheme with higher recovery rate for users.

Standardized and systematic parts are convenient for disassembly, maintenance and cleaning of equipment.

Automatic control is carried out through the terminal control system, and a humanized operation display system is configured to facilitate users to intuitively understand various data and adjust setting parameters.

The status of flushing, water shortage, full water, maintenance, etc. will be displayed on the purified water operation display system according to the actual situation, and the user will be reminded through the audible and visual alarm system.

The purified water generator has many unique functions, such as three-level password protection, fault shutdown alarm (manual reset is required), high and low pressure protection, automatic flushing, dual pipe water supply, etc.
A purified water generation system is a series of processes and equipment designed to remove impurities from a source water (such as tap water or well water) to achieve a high level of purity that meets specific standards. These systems are critical in industries and applications where water quality is paramount, such as pharmaceuticals, laboratories, healthcare, food and beverage production, and electronics manufacturing.
The primary purpose of these systems is to produce water that is free from contaminants such as:
Suspended solids: Particles like sand, silt, and rust.
Dissolved solids: Minerals, salts, and metals.
Organic compounds: Substances like bacteria, viruses, endotoxins, and other organic molecules.
Gases: Such as chlorine.
1. Product Formulation (as an Excipient):
Non-Parenteral Products: Purified Water (PW) is extensively used as a primary solvent and ingredient in the formulation of oral medications (syrups, suspensions, solutions), topical products (creams, lotions, ointments), and ophthalmic (eye drops) and nasal preparations.
Parenteral Products: Water for Injection (WFI) is the highest grade of pharmaceutical water and is essential for products administered directly into the bloodstream or other sterile body compartments. This includes intravenous (IV) solutions, injectables, and dialysis solutions. WFI must be sterile and pyrogen-free (no bacterial endotoxins).
2. Cleaning and Rinsing:
Equipment Cleaning: Both PW and WFI are used for cleaning and rinsing manufacturing equipment, pipelines, and product contact surfaces. This removes residual product, cleaning agents, and potential contaminants, preventing cross-contamination and ensuring product purity. The grade of water used often depends on the subsequent manufacturing step and the nature of the product.
Container Washing: Primary packaging components like vials, ampoules, bottles, and stoppers are washed with PW or WFI to ensure they are free from particulate matter and microorganisms before being filled with the drug product.
3. Feed Water for Further Purification:
Water for Injection (WFI) Systems: Purified Water often serves as the feed water for WFI generation systems, which typically employ distillation or advanced membrane processes like reverse osmosis coupled with ultrafiltration to achieve the stringent WFI quality standards.
Clean Steam Generation: Purified Water is used as feed water for generating clean steam (or pure steam). Clean steam is utilized for sterilizing manufacturing equipment, primary packaging components, and in processes where the steam may come into contact with the product or product-contact surfaces.
4. Laboratory Applications:
Analytical Testing: High-purity water is crucial for various laboratory tests, including quality control testing of raw materials, in-process materials, and finished drug products. This includes use in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), dissolution testing, and preparation of reagent solutions.
Culture Media Preparation: In microbiological laboratories, purified water is used to prepare culture media for testing and identifying microbial contamination.
5. Granulation Process:
In the manufacturing of solid dosage forms like tablets and capsules, purified water is often used in the wet granulation process to bind powders together, forming granules with improved flow and compressibility.
6. Coating Processes:
Purified water can be used as a solvent or vehicle for coating solutions applied to tablets and pellets.
Phone:
E-mail:
Address:
Room 1904, Building 10, No. 218, Jiqingmen Street, Jianye District, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China


